Best Practices for Cable Laying by EVIO
May 4, 2024
Inaugration at Toran Pada Village: Model Village Initiative
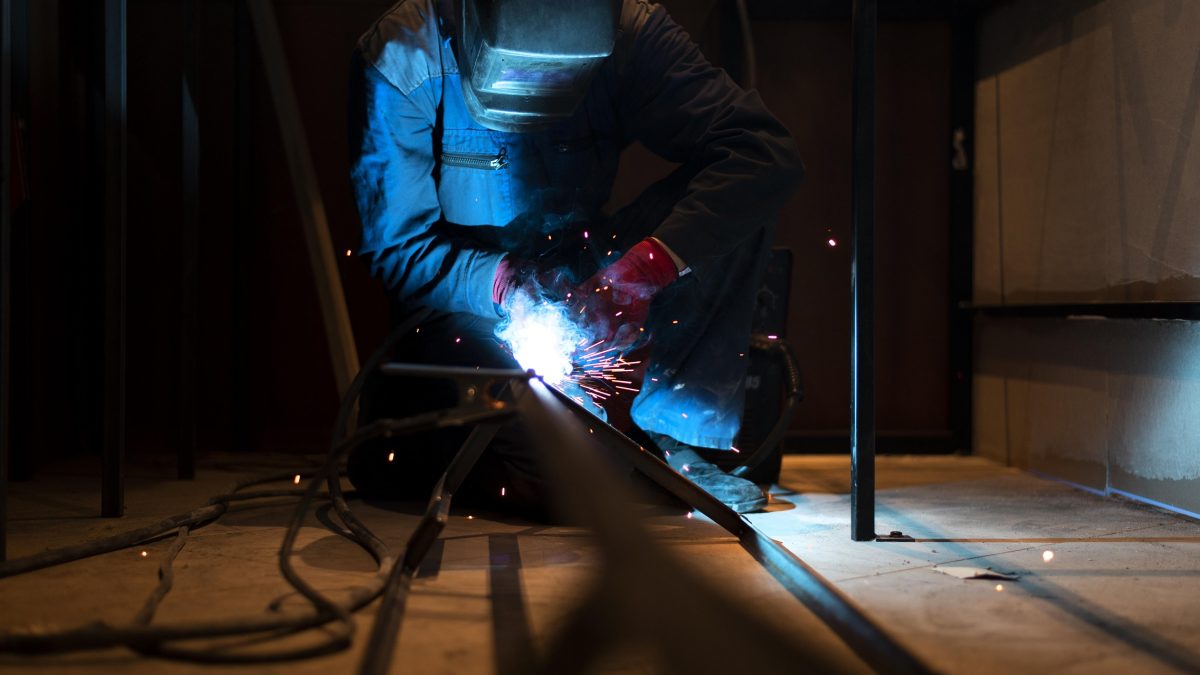
May 4, 2024Hot work—any operation that involves open flames or generates heat and/or sparks—can pose significant safety hazards if not managed correctly. This guide provides essential safety instructions to minimize risks and ensure the safety of all personnel involved in such operations. Here are the key guidelines to follow:
Pre-Work Assessment: Before beginning any hot work, conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential hazards and determine the necessary safety measures. Ensure that the area is safe for hot work operations.
Obtain Permits: Always obtain a hot work permit if required by your organization’s policies or local regulations. This permit serves as a formal check to ensure all safety measures are in place before the work begins.
Fire-Resistant Area: Ensure that the area where hot work is performed is clear of flammable materials and equipped with appropriate fire-resistant barriers if necessary.
Proper Equipment: Use the correct tools and equipment for the job, and ensure they are in good working condition. This includes personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, helmets, and fire-resistant clothing.
Trained Personnel: Only personnel trained in hot work operations and familiar with the safety procedures should perform or supervise these tasks.
Fire Watch: Assign a fire watch during and after hot work operations to monitor for any signs of sparks or smouldering materials. The fire watch should have the appropriate fire-extinguishing equipment readily available and know how to use it.
Ventilation: Provide adequate ventilation to prevent the accumulation of flammable gases or vapors produced during hot work.
Emergency Procedures: Ensure all workers are familiar with emergency procedures in case of a fire or other emergency. Practice evacuation routes and meeting points.
Post-Work Inspection: After the completion of hot work, inspect the work area and surrounding spaces for any signs of lingering sparks, smouldering materials, or residual heat that could cause a fire. The fire watch should remain in place for at least 30 minutes after the work has concluded.
Documentation and Reporting: Keep detailed records of all hot work operations, including the nature of the work, who performed it, any incidents or near misses, and the duration of the fire watch.
By adhering to these safety guidelines, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with hot work and protect their employees, facilities, and operations.