Best Practices: Earthing and Cable End Termination
May 4, 2024
Guidelines for Safe Hot Work Practices
May 4, 2024Laying cables correctly is pivotal in ensuring the longevity and reliability of an electrical installations. In this blog post, we’ll walk through the essential steps and best practices for cable laying that safeguard the integrity and functionality of cables.
Pre-Laying Insulation Check
Before beginning the laying, it’s crucial to perform an Insulation Resistance test using a hand-driven, battery-operated, or AC power-operated Megger or Insulation Tester. This test should be conducted on all new cables to ensure they are free from defects and ready for installation. Record the results for future reference and compliance purposes.
Preparing the Cable Drum
When you’re ready to lay the cables, first mount the cable drum on a pair of jacks and a shaft. This setup helps in managing the weight and aids in the unrolling process.
Correct Drum Handling
Always roll the cable drum in the direction of the arrow marked on the drum flanges. This direction is indicated to prevent the cables from twisting or kinking, which can damage the internal conductors. Remember, this method should be used only for short distances to maintain cable integrity.
Measurement and Cutting
Before cutting any cable, verify both the size and length against the project specifications. Accuracy here prevents material wastage and ensures that the cables fit perfectly in their designated paths.
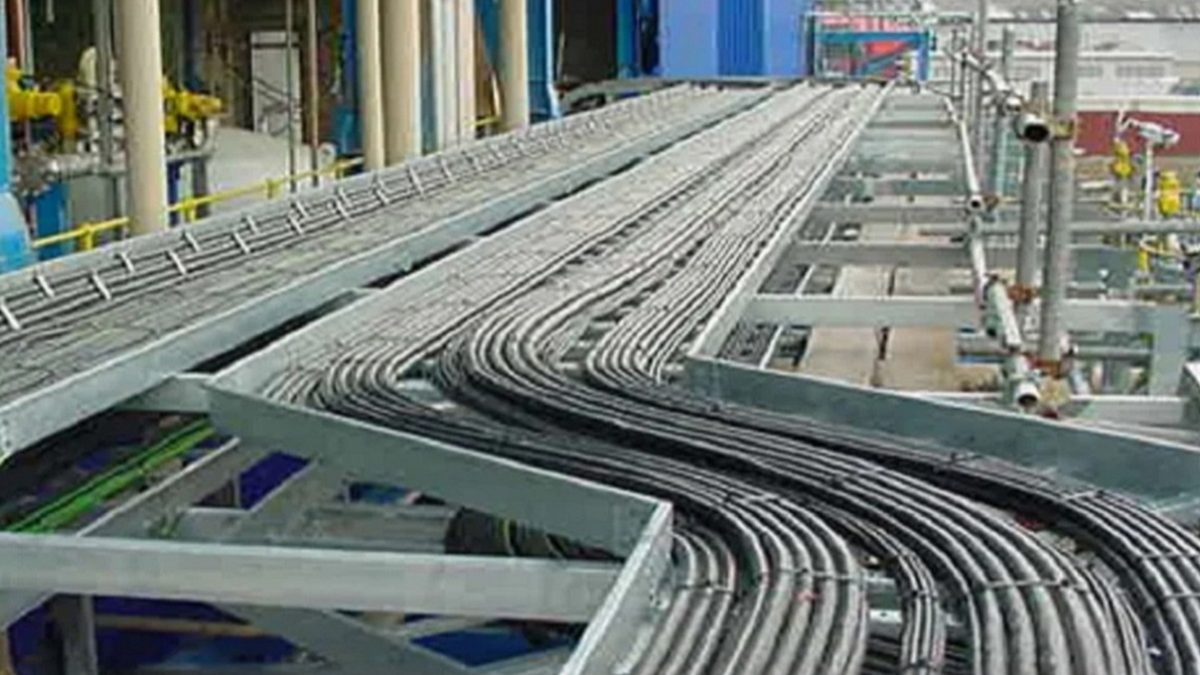
Cable Tray Considerations
When laying cables in trays, ensure that the trays are curved appropriately at right angles. This will help maintain the correct bending radius of the cable, which is crucial for preventing stress and physical damage to the cables.
Laying Cables According to Plans
Always lay cables according to the approved drawings. It’s essential to segregate power, control, and signal cables as specified in the drawings to avoid interference and potential hazards.
Adhering to Bending Radii
The bending radius is a critical aspect of cable laying. For low tension (LT) cables, the bending radius should not be less than 12 times the overall diameter of the cable. For high tension (HT) cables, it should not be less than 15 times the overall diameter. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the cables are not bent more than their capacity, thus avoiding internal damages.
Cable Identification and Management
Tag each cable with an identification tag for easy recognition and maintenance. Cables should also be dressed and aligned properly to ensure a neat and orderly arrangement that simplifies management and maintenance.
Securing Cables
Secure cables to vertical trays using clamps and use ties for horizontal trays. Avoid overlapping cables in the trays to prevent pressure and potential damage to the cable insulation.
Earth Conductor Installation
Lay the earth conductor parallel to the cables. This not only simplifies the grounding process but also ensures safety across the installation.
By following these structured steps, one can ensure that cable laying process is smooth, efficient, and compliant with industry standards. Properly laid cables lead to reduced maintenance costs, fewer failures, and a reliable electrical system that stands the test of time.